Ingrown Toenails in Allentown
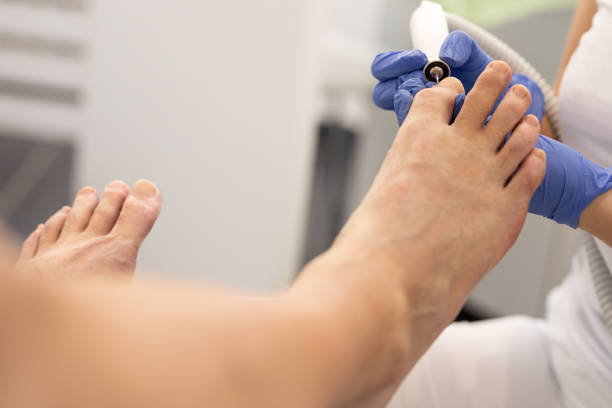
Ingrown toenails, the most common toenail impairment, are nails whose corners or sides dig painfully into the soft tissue of the nail grooves, leading to irritation, redness, and swelling.
Normally, toenails grow straight out. Sometimes, however, the corners or sides curve and grow into the flesh. Most often this occurs in the big toe, but other toes can also be affected. Left untreated or undetected, an infected, ingrown toenail can infect the nearby bone, leading to a serious infection.
Due to circulation and nerve impairment, complications of an ingrown toenail can be especially acute for diabetics. Any relatively minor injury to a diabetic patient’s foot, including corns, calluses, and ingrown toenails, may have difficulty healing and lead to a serious infection, even gangrene.
People with diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, or other circulatory disorders should avoid any self treatment and seek podiatric medical care to treat an ingrown toenail safely. Please see our page on how to prevent diabetic complications in your feet.
Any “do-it-yourself” treatments, including any attempt to remove any part of an infected toenail, should be avoided. Nail problems should always be evaluated and treated by your podiatrist, who can diagnose the problem, and then prescribe medication or another appropriate course of treatment.
Symptoms of an ingrown toenail:
- Pain and tenderness along one or both sides of the toenail
- Redness around the toenail
- Swelling of the toe around the toenail
- Infection of the tissue surrounding the toenail
***If you suspect that you have an infected ingrown toenail, immerse your foot in a warm salt water soak or a basin of soapy water, then apply an antiseptic and cover with a bandage. Make an appointment with the PA Foot and Ankle Associates office for a complete diagnosis and treatment plan.
Ingrown toenails may be caused by:
- Cutting toenails too short or not straight across. (Use nail clippers to trim them straight across, no longer than the tip of the toes. Do not round off corners)
- Heredity – unusually curved toenails
- Wearing shoes that force your toes together, crowding your toenails
- Repeated trauma to the foot, causing injury to the toenail
Treatment for ingrown toenails:
A podiatrist will resect (partially remove) the ingrown toenail and may prescribe a topical or oral medication to treat the infection. If ingrown toenails are a chronic problem, a procedure to permanently prevent ingrown toenails may be recommended.
Michael, a student at Northwestern Lehigh High School, tells why he chose us for treatment of his ingrown toenails.


